Level of Coaching
Coaching is a profession designed to help individuals or organizations achieve their goals, improve their performance, and foster personal growth. It provides a supportive and non-judgmental space for individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Coaches can specialize in various fields, including business, sports, education, and personal development. Business coaches, in particular, help professionals and organizations enhance their skills, driving them towards success through structured coaching programs.
Coaching certifications, such as those offered by the International Coach Federation (ICF), Certified Professional Coach (CPC), and Certified Coach (CC), are credentials that establish a coach’s expertise and competency. These certifications are important for building trust with clients and enhancing a coach's credibility. The ICF, for example, has three key levels of certification: Associate Certified Coach (ACC), Professional Certified Coach (PCC), and Master Certified Coach (MCC). Each of these levels requires specific coaching experience, training hours, assessments, and mentor coaching.
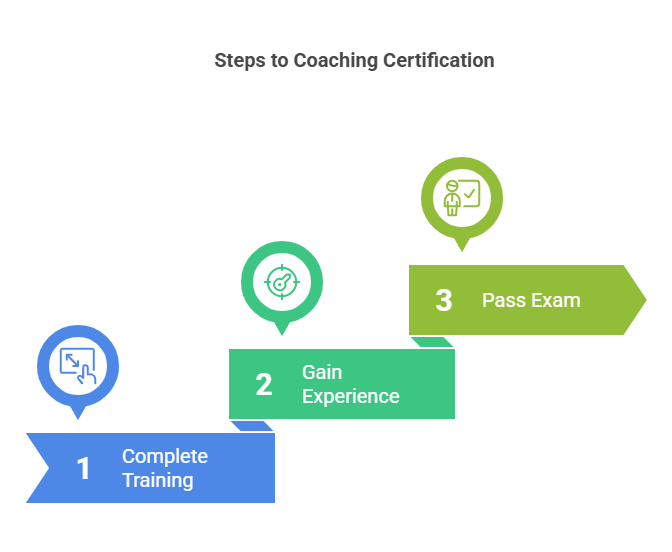
The Coaching Certification Process
Becoming a certified coach typically involves completing a coach-specific training program, gaining significant coaching experience, and passing a certification exam. For example, ICF requires at least 60 hours of training and 100 hours of coaching experience to become an ACC, along with a certification exam. Other certifications, like the CPC and CC, also require completing training programs and passing exams but may have different requirements.
Training programs for coaches focus on building essential coaching skills and ethics. They often include topics such as coaching frameworks, client communication, and business development. Some programs may even include mentor coaching, where experienced coaches guide less experienced ones to help develop their skills and confidence.
Advanced Coaching Certifications
For coaches looking to advance their careers, obtaining certifications like the PCC and MCC is essential. These advanced credentials require more extensive training and experience. They offer a higher level of expertise, and coaches who achieve these certifications gain recognition in the industry. Advanced certifications not only boost a coach’s credibility but also open up opportunities for career advancement.
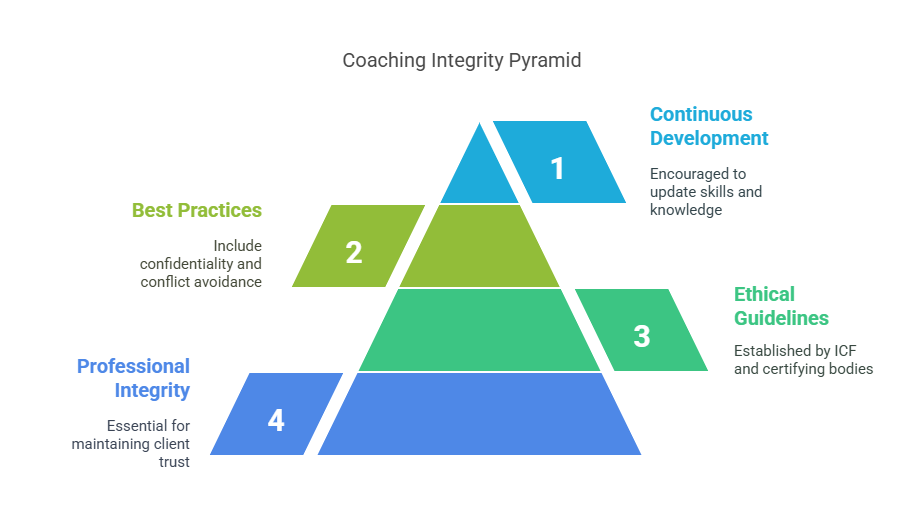
Ethical Considerations in Coaching
A coach’s professional integrity is essential in maintaining trust with clients. The ICF and other certifying bodies have established core competencies and ethical guidelines to help coaches adhere to best practices. These include maintaining confidentiality, avoiding conflicts of interest, and respecting client autonomy. Coaches are also encouraged to continuously develop their skills to stay up to date with industry standards.
The Role of Technology in Coaching
Technology has transformed coaching practices, providing coaches with new tools to connect with clients and deliver services. Online coaching platforms, video conferencing tools like Zoom, and mobile apps are widely used to deliver coaching remotely. Additionally, social media helps coaches build their networks and reach new clients. However, coaches must be aware of the ethical implications of technology use, such as maintaining confidentiality and ensuring data security.
Maintaining Your Certification
To keep coaching certifications active, coaches must engage in continuous professional development. The ICF, for example, requires coaches to complete Continuing Education Units (CEUs) to maintain their certification. Adherence to ethical guidelines and consistent coaching practice is also essential to retain certification status.
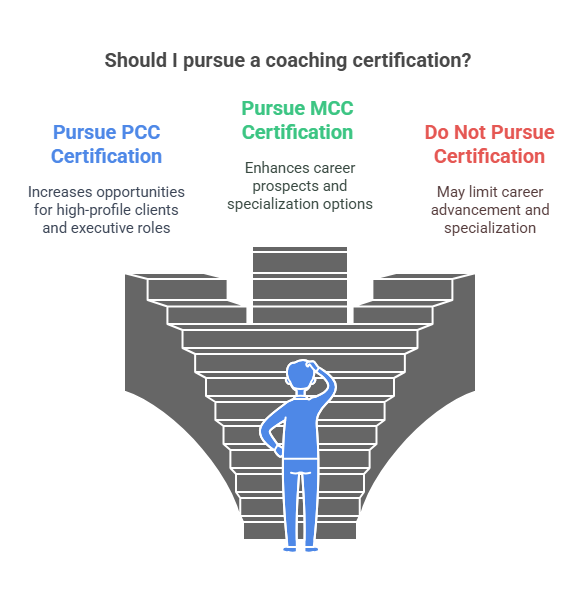
Career Advancement through Coaching Certifications
Coaching certifications can significantly enhance a coach's career, leading to increased client trust, higher fees, and more career opportunities. Coaches who hold advanced certifications like the PCC or MCC have greater chances to work with high-profile clients or take on executive roles in coaching organizations. Certification may also allow coaches to specialize in areas such as business or executive coaching.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Coaching Certification
Aspiring coaches often face challenges, such as limited experience, insufficient training, or difficulty passing exams. Overcoming these obstacles involves seeking mentor coaching, completing additional training, and refining coaching practices through experience. Successful coaches are those who remain committed to lifelong learning.
6 Less-Known Facts About Coaching Certifications
Different Coaching Streams: Coaching certifications are not just for business coaches. There are specialized certifications for areas like life coaching, career coaching, executive coaching, and health and wellness coaching.
Coaching Hours Can Be Flexible: Some certification programs allow for coaching hours to be spread over several years, offering flexibility to those who may be transitioning into coaching while working full-time in other fields.
International Recognition: Many coaching certifications, especially those from organizations like ICF, are recognized globally, allowing coaches to practice internationally without needing additional credentials.
Mentor Coaching Requirement: The ICF certification requires coaches to engage in a minimum of 10 hours of mentor coaching. This ensures they are aligned with industry best practices and core competencies.
Technology’s Influence on Ethical Standards: While technology enhances the coaching process, it also poses challenges. The rise of virtual coaching emphasizes the importance of secure platforms and protecting client confidentiality in digital spaces.
ICF's Code of Ethics: Coaches must adhere to a strict code of ethics, which includes not only client confidentiality but also guidelines on maintaining objectivity and avoiding dual relationships (such as coaching friends or family).
Conclusion
Coaching certifications are crucial for anyone serious about pursuing coaching as a profession. They provide structure, credibility, and a clear path to professional growth. From entry-level certifications like ACC to advanced certifications like MCC, the coaching journey is built on continuous learning, ethical practices, and ongoing career development. Whether you're just starting or advancing your career, coaching certifications can provide the foundation for long-term success in this fulfilling field.
ANHCO and ANHCO Health Coach Certification provide comprehensive training for aspiring coaches, focusing on evidence-based coaching techniques and holistic health principles. These certifications equip professionals with the skills needed to guide clients toward healthier lifestyles while maintaining ethical coaching standards. With ANHCO’s emphasis on practical experience and professional credibility, certified coaches gain a competitive edge in the health and wellness industry.
FAQS
-
Coaching levels typically include beginner, intermediate, advanced, and elite coaching, depending on the skill level and experience of the individual being coached.
-
Your coaching level depends on your expertise, experience, and ability to guide others effectively. Certifications, years of experience, and client results can help define your level.
-
Description text goes here
-
Higher-level coaching often requires formal certifications, extensive experience, and proven success in helping clients achieve their goals.
-
Yes, with continued learning, experience, and professional development, coaches can progress to higher levels of coaching.
-
Elite or master-level coaching is the highest tier, where coaches work with top professionals, athletes, executives, or individuals seeking high-performance results.