Mastering Motivational Interviewing: A Key Skill for Certified Health Coaches
Motivational Interviewing (MI) is a powerful, client-centered communication style that helps health coaches support clients in making meaningful lifestyle changes. This technique, originally developed by psychologists William R. Miller and Stephen Rollnick, is widely used in health coaching, therapy, and healthcare. In 2025, with the rise of virtual coaching and AI-assisted wellness programs, MI remains essential for fostering sustainable behavior change.
In this guide, we'll explore the principles, techniques, and updated insights on MI, including six lesser-known facts, real-world applications, and FAQs.
What Is Motivational Interviewing?
Motivational Interviewing is a structured yet flexible method that helps clients overcome ambivalence and take action toward their health goals. Rather than instructing clients on what to do, MI encourages self-discovery and empowerment.
At its core, MI is built on four key principles:
Express Empathy – Understanding clients’ struggles without judgment.
Develop Discrepancy – Highlighting the gap between current behaviors and desired outcomes.
Roll with Resistance – Avoiding confrontation and instead guiding clients to explore change.
Support Self-Efficacy – Reinforcing clients' belief in their ability to change.
The Spirit of Motivational Interviewing
MI is not just a set of techniques—it’s a mindset that health coaches adopt to guide their clients effectively.
1. Collaboration Over Authority
Health coaches act as partners rather than experts dictating change. Clients are more likely to embrace transformation when they feel heard and supported.
2. Evocation Over Imposition
Rather than telling clients what to do, MI helps them uncover their own motivations for change. This makes behavior shifts more sustainable.
3. Respect for Autonomy
Clients are in control of their decisions. The role of a coach is to provide guidance, not force solutions.
The Four-Step Process of Motivational Interviewing (Expanded)
1. Engaging – Building the Foundation of Trust
Engaging is the very first and arguably the most crucial phase of Motivational Interviewing. Without a strong connection, clients may not feel safe enough to open up about their struggles or goals.
What It Involves:
Using active listening to demonstrate genuine interest.
Creating a non-judgmental, empathetic space where clients feel seen and heard.
Asking open-ended questions to learn about the client’s values, lifestyle, and concerns.
Reflecting on their words to show you understand them.
Example: Instead of jumping into goal setting, start by saying:
"Tell me a little about your day-to-day life. What does a typical day look like for you?"
Why It Matters: Clients who feel understood are more likely to stay engaged in the process and trust the coach’s guidance as they navigate change.
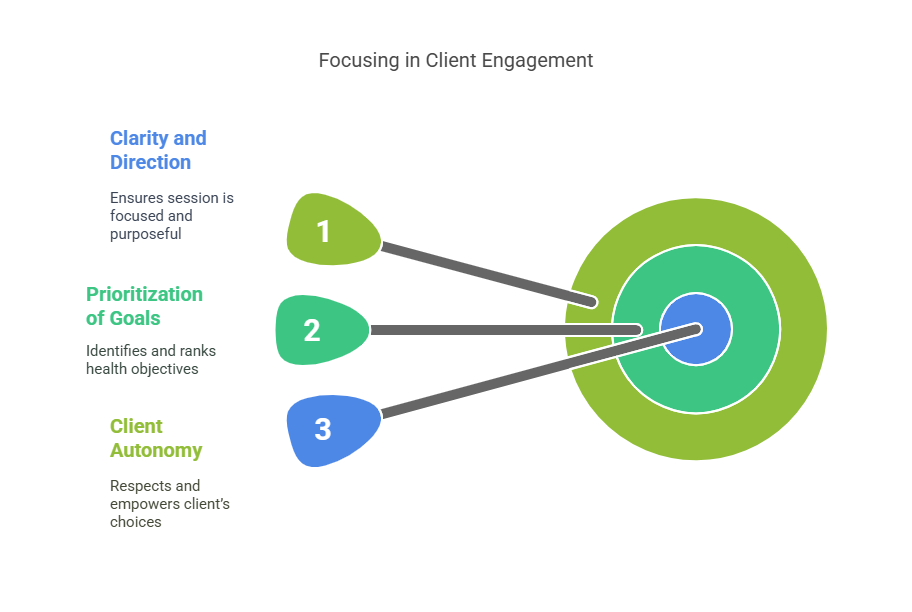
2. Focusing – Clarifying the Direction of Change
Once engagement is established, the next step is to narrow the conversation toward specific goals. Focusing helps you and the client align on a shared purpose, without rushing into problem-solving.
What It Involves:
Collaboratively identifying areas the client wants to change.
Exploring and prioritizing which health goals matter most.
Avoiding coach-driven agendas—let the client lead the way.
Example: "You mentioned wanting to feel more energetic and also eat healthier. Which of those feels more important to start with right now?"
Why It Matters: Focusing ensures the session doesn’t feel scattered. It provides clarity and direction, while still respecting the client's autonomy and readiness.
3. Evoking – Uncovering Internal Motivation
Evoking is the heart of Motivational Interviewing. This stage helps clients discover and verbalize their own reasons for change rather than responding to external pressure.
What It Involves:
Asking thought-provoking, open-ended questions.
Using reflections and affirmations to reinforce their insights.
Gently exploring ambivalence (e.g., “Part of you wants to exercise more, and part of you feels overwhelmed by it.”)
Tools to Use:
Change talk: Encourage clients to talk about their desire, ability, reasons, and need for change.
Decisional balance: Weighing the pros and cons of changing vs. staying the same.
Example: "What would it mean for you to feel more energized throughout your day? How would that change things for you?"
Why It Matters: When clients articulate their own reasons for wanting to change, it significantly boosts motivation and follow-through.
4. Planning – Turning Motivation Into Action
Once motivation is strong, it’s time to move into the planning phase. Here, the focus is on helping the client design a concrete, manageable plan to reach their goals.
What It Involves:
Collaboratively developing realistic, measurable steps.
Identifying potential barriers and creating backup strategies.
Reinforcing confidence and readiness to begin.
Example: "You mentioned that preparing meals ahead of time could help you eat healthier. What’s one small step you could take this week to start that process?"
Why It Matters: Without a clear action plan, motivation can fade. Planning bridges the gap between desire and action, making change feel achievable and structured.
Practical MI Techniques for Health Coaches
1. Open-Ended Questions
Encourage deeper thinking and self-reflection:
“What are some challenges you’ve faced in making this change?”
“What would success look like for you?”
2. Affirmations
Reinforce positive behaviors and strengths:
“You’ve made great progress by recognizing what’s important to you.”
“I appreciate your commitment to this journey.”
3. Reflective Listening
Help clients feel understood by paraphrasing their concerns:
Client: “I find it hard to stick to a routine.”
Coach: “It sounds like consistency has been a challenge for you.”
4. Summarizing
Reinforce key points and next steps:
“So far, we’ve discussed your goal of improving your diet, and you’ve identified that meal prepping might help. Let’s explore how to start.”
Case Studies: Motivational Interviewing in Action
Case Study 1: Overcoming Exercise Resistance
Client: Sarah, 35
Challenge: Struggles with time management and motivation for exercise.
MI Approach:
Engaged Sarah by discussing her daily routine.
Focused on her personal fitness goals.
Evoked motivation by exploring her deeper reasons for exercising (e.g., more energy for family).
Developed a flexible workout plan starting with 10-minute sessions.
Outcome: Sarah felt more confident and started incorporating small workouts into her routine.
Case Study 2: Addressing Dietary Changes
Client: John, 50
Challenge: Feels overwhelmed about making dietary adjustments for diabetes.
MI Approach:
Built trust by validating his concerns.
Focused on specific dietary habits.
Evoked motivation by discussing long-term health benefits.
Created a plan for gradual dietary changes without eliminating favorite foods.
Outcome: John successfully improved his eating habits and saw better blood sugar levels.
Six Lesser-Known Facts About Motivational Interviewing
MI Is Now Used in AI-Powered Coaching
AI-driven health apps are integrating MI techniques to provide personalized coaching and motivation.It Was Originally Designed for Addiction Treatment
While now widely used in health coaching, MI was first developed to help individuals struggling with substance use disorders.MI Is Effective in Virtual Coaching
With the rise of telehealth, MI has been adapted for online coaching, proving just as effective as in-person interactions.It Works Even When Clients Aren’t Ready to Change
Unlike traditional coaching, MI doesn’t require immediate readiness—it's designed to gently guide clients toward change.MI Improves Retention in Health Coaching Programs
Clients working with MI-trained coaches are more likely to stay committed to their health programs compared to those receiving directive coaching.MI Can Be Used for Team Motivation
MI isn’t just for individual coaching—it's being used in corporate wellness programs to enhance team performance and motivation.
Final Thoughts
Mastering Motivational Interviewing is an invaluable skill for health coaches in 2025. Whether coaching in-person or online, MI helps foster meaningful, lasting change by prioritizing empathy, collaboration, and autonomy.
For health coaches looking to enhance their impact, investing in MI training is a game-changer. With the increasing demand for client-centered coaching, MI remains one of the most effective techniques for guiding individuals toward healthier, more fulfilling lives.
ANHCO is a mission-driven organization dedicated to empowering individuals to lead healthier lives through certified health coaching. With a focus on holistic well-being, ANHCO blends science-based strategies with human-centered support. Their goal is to make sustainable health change accessible to everyone.
The ANHCO Health Coach Training Program is designed for aspiring coaches who want to make a real difference. It combines Motivational Interviewing, behavioral science, and practical coaching tools into a powerful, hands-on curriculum. Graduates walk away confident and job-ready, whether they choose private practice or employment.
What sets ANHCO apart is its commitment to both heart and evidence. The program nurtures coaches who are not only skilled but also deeply compassionate and culturally aware. With flexible learning options and ongoing mentorship, ANHCO prepares you to thrive in a growing, meaningful profession.
FAQS
-
Motivational interviewing is a client-centered communication technique that helps individuals explore their own motivations and overcome ambivalence toward behavior change.
-
MI helps coaches guide clients toward making lasting changes by encouraging self-reflection, building confidence, and fostering internal motivation rather than using pressure or advice-giving.
-
Unlike directive coaching, MI emphasizes active listening, empathy, and asking open-ended questions to help clients discover their own reasons for change at their own pace.
-
Yes. MI is especially effective for supporting behavior change in areas like weight management, nutrition, exercise, smoking cessation, and managing chronic conditions.
-
While not always required, MI training is highly recommended. It enhances a coach’s effectiveness and is often included in advanced certifications and continuing education.
-
You can improve by attending MI workshops, practicing with peers, studying real-life coaching scenarios, and getting feedback from experienced mentors or trainers.